In a computer system, the power supply is responsible for converting standard household electrical current into a low DC voltage that can be used by the machine while it is running, and is responsible for turning on the various internal components of the computer.
Typically common power supply problems are a fan that doesn't spin when turned on and a completely dead computer system. In some cases, frequent reboots of the machine occur, caused by a faulty power supply that is no longer able to supply direct current to the computer. Such symptoms in the behavior of equipment indicate that an urgent check of the power supply should be performed.
Types of power supply failures

Most common power supply problems:
- Any power-on failure, system failure or lockout.
- Sudden reboot and intermittent blocking of normal operation.
- Periodic flash memory check.
- Simultaneous stopfan and hard drive.
- Temperature rise and overheating due to fan failure.
- Small power spikes cause the entire system to reboot.
- Damage to electrical equipment.
- The presence of static discharges disrupts the system.
Specialists believe that IP is a weak link in the functioning of the system.
Especially dangerous phenomena that indicate a breakdown of the IP:
- system completely dead (no fan, no cursor);
- smoke;
- bloated switches.
If there are suspicions of problems with the power supply, the computer's power supply must be checked.
Methods for checking power
Testing the DC output voltage with a DMM can help identify any potential problems and determine if the power supply is working.
Safety measures:
- Always use multimeter leads to touch wires and terminals - never touch parts with your hands.
- If it is not possible to hold the wires or terminals with it, use a stand or clamp to fix them so that you do not hold them with your hand.
Required materials:
- multimeter;
- power supply;
- screwdriver;
- paperclip;
- computer;
- grounding bracelet.
First way
Sequence:
- The very first test to be performed is to check the condition of the electrical outlet. Checking the power supply begins with a visual inspection of it to make sure it is in good condition and not the source of the problem. Alternatively, connect a table light to it to make sure it is working and providing sufficient quality of electricity.
- Turn on the multimeter and set the voltage from 120 to 240 volts, depending on the standard mains voltage in the house.
- Turn off the computer and disconnect it from the network. Make sure it is properly grounded before opening the case.
- Remove the computer cover. Visually inspect the unit and its connectors for any signs of damage or burns.
- Check your computer connectors. They are usually found on the motherboard, hard drive, floppy drive, CD or DVD drive, and other accessory fans.
- Look for a power connector that is not in use. If they are not available, simply unplug any used connector.
- Turn on the multimeter to a DC voltage in the range of 12 volts or less.
- Plug the computer back in and turn it on.
- Hold the power connector (not the wires) and locate the black and yellow wires. Insert the black tester lead into the hole corresponding to the black wire and the red lead corresponding to the yellow wire.
- Load to test the power supply +12 volts. Make sure your multimeter is showing the correct voltage.
- While holding the black wire in its current position, move the red wire to the hole that matches the red wire of the connector. Indicationshould be +5 volts on it.
- If it shows a different reading or nothing during step 7 and step 8, the power supply is defective and needs to be replaced immediately.
- If the readings are correct, then the problem of power failure may be due to a malfunction of the computer's motherboard.
Second way
Checking the power supply with a multimeter in this way is a general test for the he alth of the source:
- Turn off the computer and switch on the back of the power supply.
- Disconnect power from outlet.
- Open the computer case.
- Disconnect power cables from all components inside the case.
- Check every cable from the power supply to the component to make sure everything is disconnected properly. Remember how everything was connected so that you can reassemble it later.
- You can use a paperclip to test the power supply by pretending it is on. To do this, bend the paperclip into a "U" shape. This paperclip will act as pins that are inserted into the power supply and signal "Power ON".
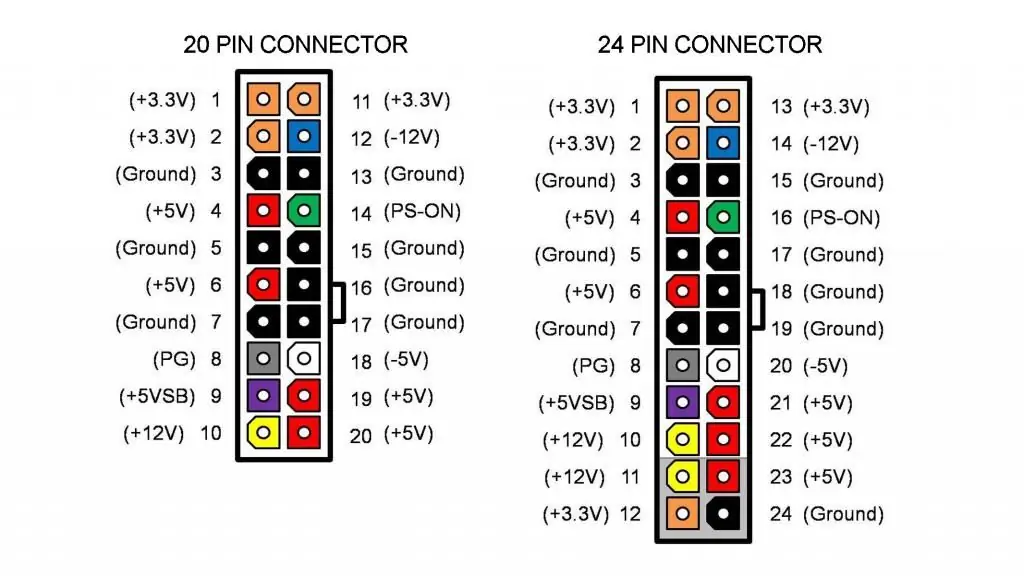
- Find the 20/24 male connector connected to the motherboard, this is usually the largest one.
- When checking the computer's power supply, close its contacts. Find black and green pins (15 and 16). Insert a paperclip into the green pin (there should be only one) and the adjacent black pin. Before doing this, double check that the power has been completely disconnected from theelectrical outlet and is not connected to any computer components. The green pin is usually number 15 on the pin chart.
- Insert a paperclip. Connect the power supply back to the outlet and turn on the switch at the back of the unit.
- Check the fan. When the power supply receives power, the fan rotates. This allows you to understand that it works. If it doesn't turn on at all, double check all contacts (after unplugging) and try again. If it still does not turn on, then most likely the unit is not operational.
This test will not tell you what standard parameters the unit is working with, it will only confirm that voltage is being supplied to it.
Third way
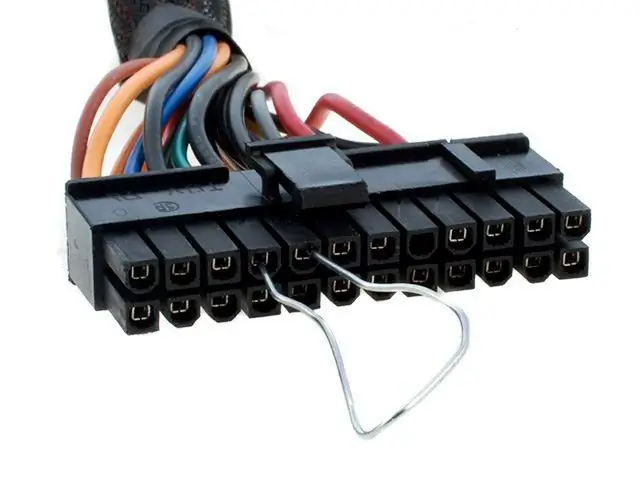

Checking the power supply in this way sets the actual operating parameters of the IP:
- Check the output through the software. If the computer is functioning and the operating system is loading, try using the software to check the power supply output.
- Check the readings to make sure they match the data given in the manufacturer's instructions.
- Turn off the computer, unplug the power outlet, and press the power switch on the back.
- Disconnect all components from the power supply.
- Checking the voltage of the power supply using testing. Connect the test block to connector 20/24. Connect the power supply to the outlet and turn it on, it should automatically work, and the power indicator will light up. Check voltage. The 20/24 connector will have several indicators, but there are 4 main measurements you need to look for: +3, 3VDC, +5V, +12V, -12V.
- Make sure the voltages are within tolerance. If any of the readings is outside the parameters of this range, then the IP is inoperative and needs to be replaced.
- After it is established that the main connector is outputting power correctly, check each of the other connection cables.
- Turn off and on the PI between each measurement.
- When checking, close the power supply: find the green contact on the 20/24-pin connector. Insert a paperclip into the green pin (pin 15) and into one of the adjacent black pins.
- Turn on IP. Set your multimeter to VBDC. If it is on autorange, set the range to 10V.
- Connect the negative probe to the ground (black) pin on the connector and the positive probe to the first output to test.
- Check the voltage: if any of the parameters is out of range, the power supply is faulty.
- Repeat the process for each of the peripheral connectors. Refer to the specific pin diagrams for each connector to find out which ones to test.
- Assemble the computer. Make sure all devices are properly connected and all motherboard connectors are properly installed.
Once you've finished assembling your computer, you can try turning it on. If you still experience computer errors or your computer does not start, go toother troubleshooting steps.
Reverse probing power connectors

The following table shows voltage ranges within tolerances.
| Required voltage | Free tolerance | Free tolerance | Tight tolerance | Tight tolerance |
| minimum (-10%) | max (+ 8%) | minimum (-5%) | max (+5%) | |
| + 3.3V | 2.97V | 3.63V | 3, 135 | 3, 465 |
| +/- 5.0V | 4.5V | 5.4V | 4, 75 | 5, 25 |
| +/- 12.0V | 10.8V | 12.9V | 11, 4 | 12, 6 |
Best Computer Test Software - 2018
Hardware failures happen from time to time, it is necessary to prevent such events with the help of specialized software. Checking your computer's power supply is an important step when it starts to fail. A faulty source can be at the root of all problems, even those that users don't expect, such as spontaneous reboots, random lockups, and even serious ones.informational error messages.
AIDA64 Extreme (recommended)

This is an advanced system diagnostic utility that can collect important information about the hardware configuration and power supply of your computer. The software allows you to test the capabilities of the system memory, FPU and CPU by running complex tests. The setup process is quick and simple. AIDA64 Extreme comes with a user friendly interface. All data related to computer components is divided into separate categories. This software is designed for more advanced users thanks to its extensive set of sophisticated features.
OCCT 4.5.1
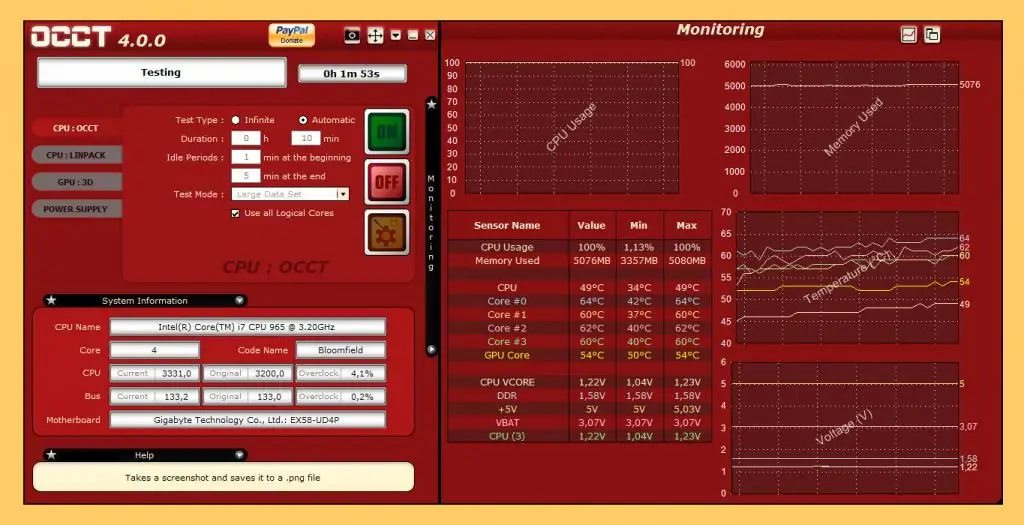
This power supply tester is a powerful and free (for personal use) stability tester. Running the program immediately shows all the useful information about the PC and GPU, as well as a series of graphs showing how the system temperature changes, processor voltages, RAM usage and other details. And if they don't detect any issues on their own, OCCT can run tests for CPU, GPU, or power usage, again giving you detailed insight into how temperatures, voltages, and other system data might respond in a critical situation.
OCCT will in many cases stop testing if certain measured values are too high. The latest version is 4.5.1. The program is free. Platforms: Windows XP, Windows Vista (32-bitversion), Windows 7 (32-bit), Windows Vista (64-bit), Windows 7 (64-bit), Windows 8, Windows 10.
Open Hardware Monitor

This is an efficient program that tests the state of the IP.
The application provides all the information in a simple tabular way, making it easy to track the status of your computer over a long period of time. It is designed for users of different skill levels. This computer power supply tester monitors primary system sensors for the most common chips and provides the most accurate power supply data.
Setting up the program is an easy task and does not require any specific configuration. The program comes with a simple interface, automatically starts monitoring sensors on startup. All data can be exported to a text document. This tool provides a simple solution for finding problems in real time. The paid version of HWMonitor Pro on the official HWMonitor website includes additional testing features.
PC Wizard

This is a system analyzer that is very effective in power testing and provides complete data on equipment weaknesses. After running this program, it will take some time to detect all the hardware installed on the computer.
A useful tool for analyzing hardware data, including power supply information. itquite a complex program aimed mainly at more advanced users.
The presented review includes the best programs that can analyze and provide accurate information about the power supply of the system and much more. To test the full range of application features and analyze which ones are best for the user of the system, you can go to the official websites of the programs and download the desired software.






