System on a chip is a small chip with all necessary electronic components and circuits. In English literature, the term SoC (system-on-a-chip) is used. The system in the sound detection device may include an ADC, an audio receiver, a memory, a microprocessor, and a user I/O logic control on a single chip.
In medicine, an SoC system based on nano-robots can act as programmable antibodies to delay early illnesses. Chip-based video devices can help blind people by allowing them to receive an image, and SoC audio devices can make deaf people hear. The system-on-a-chip is evolving along with other technologies such as SOI (silicon on insulator).
Definitions of terms
The SoC system combines the required electronic circuits of various computer components on a single integrated chip (IC). An SoC is a complete substrate electronic system that can contain analog,digital, mixed or RF functions. Its components typically include a graphics processing unit (GPU), a central processing unit (CPU), which can be multi-core, and system memory (RAM).
Because the system-on-a-chip includes both hardware and software, it consumes less power, has better performance, requires less space, and is more reliable than multi-chip systems. Most system chips are included in mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets today.
The System-on-a-Chip is specifically designed to meet the standards for incorporating the required electronic circuitry of numerous computer components onto a single integrated chip. Instead of a system that assembles multiple chips and components onto a PCB, an SoC creates all the necessary circuitry in a single device.
SoC challenges include higher prototyping costs, architecture, and more complex debugging. ICs are not cost effective. However, this may change as technology advances.
Required microchipping parameters

System on Chip SoCs are very complex devices. For example, Qualcomm's Snapdragon 600 system-on-a-chip is the SoC that was used in the old Samsung Galaxy smartphone.
People want to be able to use their smartphones to surf the Internet, listen to music, watch videos, use GPS navigation, take photos and videos, play games, access social networks. All these featuresare provided not only with a good processor, but also with a powerful graphics chip System on Chip SoC, fast wireless Bluetooth chipset, support for connecting to 4G networks. All this should work with the least energy consumption.
The solution is to miniaturize everything that can be installed. Devices should be as compressed as possible and placed compactly on a smaller surface. The consequence of this is higher processing power and lower power consumption. This is exactly what SoC offers.
System-on-Chip Design
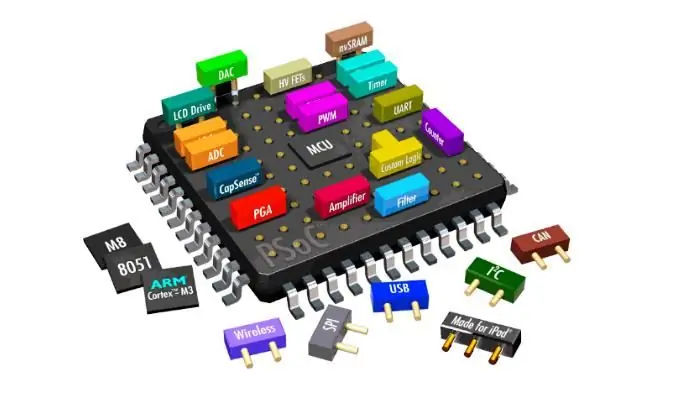
Conceptually, there are three levels of design strategy for functional chips. The first level is the symmetry of the point group. It dictates the presence or absence of a certain physical response and anisotropy of the crystal. Therefore, it can be used to search for and shield new functional crystals.
Point group symmetry is a necessary requirement, but not a sufficient condition for a functional crystal. For an SNK system-on-a-chip to exhibit a particular property, it must be complemented by a second level of design strategy-space group structure or symmetry.
Finally, to enhance or optimize the response, there is a third level of molecular engineering design strategy that involves fine-tuning the electronic or magnetic structures of the building blocks of atoms, molecules, and crystal clusters.
Componentsmobile devices
An SoC system-on-a-chip can have various elements, depending on its purpose. Since the vast majority of SoCs are used on smartphones, we offer a list of the most common components of such devices:
- CPU is the core inside the SoC. This is the part that is responsible for making most of the calculations and decisions. It receives input from other hardware components and software and provides appropriate output responses. Without the CPU, there would be no SoC. Most processors today have two, four or eight cores inside.
- GPU - shortened for graphics processing module. It is also called a video chip. The GPU is responsible for 3D gaming as well as the neat visual transitions that are visible in the interface of any device using a single-chip system.
- RAM Memory - all computing devices need memory to work. To be able to run applications and software data, you must use them. To do this, the system-on-a-chip must have RAM.
- ROM - Any device must have ROM memory to store software such as firmware or the operating system it runs on.
- Modem - a smartphone will not be a phone if it cannot connect to radio networks. Modems take care of the network or cellular connection.
In addition to the processor and memory, other SoCs may include PCIe interfaces designed forconnecting radio transceivers, SATA interfaces, or USB devices.
Chip design
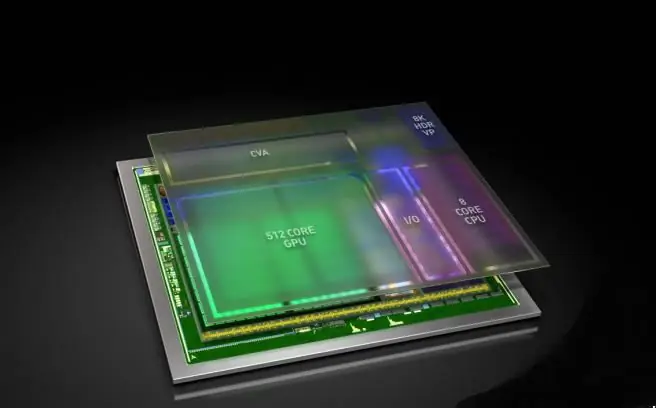
Systems on a chip must have semiconductor memory blocks to perform their calculations. Depending on the application of the SoC, memory can form a hierarchy of memory and cache. This is common in the mobile computing market, but is not required in many low-power embedded microcontrollers.
Memory technologies for SoCs include read-only memory (ROM), random access memory (RAM), electrically erasable programmable ROM (EEPROM), and flash memory. As with other computer systems, RAM can be divided into the relatively faster but more expensive static RAM (SRAM) and the slower but cheaper dynamic RAM (DRAM), as in the system-on-a-chip pictured in this article.
External interfaces

SoCs include external interfaces, typically for communication protocols. They are often based on industry standards such as USB, FireWire, Ethernet, USART, SPI, HDMI, I2C, and more. Wireless network protocols such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, 6LoWPAN, and near field communications may also be supported.
If required, SoCs include analog interfaces for signal processing. They can interact with various types of sensors or actuators, including smart converters. They may also contact specificmodule applications or be internal to the SoC, for example, if an analog sensor is built into the SoC and its readings must be converted to digital signals for mathematical processing.
Digital Signal Processors
Digital signal processors (DSPs) are often included in systems on a chip. They perform operation signal processing for sensors, actuators, data acquisition, data analysis and multimedia processing. DSP cores typically have a very long instruction word (VLIW) and unidirectional instruction set architecture, so they are amenable to exploiting parallelism.
4DSP cores most often contain application-specific instructions and are the processors of the ASIP application-specific manual set. Such instructions correspond to specialized functional units.
Typical DSP instructions include multiple accumulation, fast Fourier transform, smooth multiplication, and convolution. As with other computer systems, SoCs require clock sources to generate clock signals, control the execution of functions, and provide timing context to signal processing applications if needed.
Popular time sources are crystal oscillators and phase-locked loops. SoCs also include voltage regulators and power management circuits.
The difference between SoC and CPU

Once upon a time, many people thought that the CPU was completely isolated from the monitor. Now many understand that the CPU is only a tiny part,and a computer is made up of many parts.
System on a chip is an electronic circuit board that integrates all the necessary components in a computer and other electronic systems. These include the GPU, CPU, memory, power management circuitry, USB controller, wireless radios, and more. These components are soldered on the motherboard, which is different from conventional computers, parts of which can be replaced at any time.
You could say that a system on a chip (SoC) is what happens when Vector from Despicable Me uses "beam compression" on a full-fledged computer. With the power of miniaturization, the System on a Chip is a functional computer that has been compressed to fit on a single silicon chip.

Where the chips are used
SoC is typically tiny and doesn't take up much space inside an electronic device, making it ideal for smaller devices. It combines many different parts on a single chip, meaning that its manufacturer doesn't have to spend time, money, and resources laying down significant physical parts and building long circuits, which in turn means lower production and costs. Systems on a chip are much more efficient than those with dedicated individual components such as a desktop PC or laptop. SoC can run on batteries for a longer time.
Traditional approaches to electronics have been about creating systems that run on individualindependent parts. Examples are computers and laptops. However, the constant miniaturization of everything around means they are increasingly relying on smaller, more energy efficient systems on a chip. Smartphones, tablets and even IoT (Internet of Things) devices are proving that systems on chips are an important part of the future of all electronics.
Intel Pentium N3710 Device

The Pentium N3710 is a 64-bit quad-core system-on-a-chip designed by Intel and introduced in early 2015 as part number 3710. Based on the Airmont microarchitecture. This chip operates at 1.6GHz with mode up to 2.57GHz. SoC includes HD Graphics 405 GPU which has 16 execution units and runs at 400 MHz
N3710 system-on-chip architecture details:
- Designer - Intel.
- Manufacturer - Intel.
- Model number - N3710.
- Part number - FH8066501715927
- Scope - mobile.
- Issue - March 2015
- Pentium N3000 series.
- Frequency - 1600 MHz.
- Speed - 2567 MHz (1 core).
- Bus type - IDI CPUID 406C4.
- Microarchitecture - Airmont.
- Main name is Braswell.
- Technology - CMOS.
- Word size - 64-bit.
- Maximum processors - uniprocessor.
- Maximum memory is 8 G.
- PP temperature 0 C - 90 C.
- IntegratedGPU graphics information - HD Graphics 405.
- The maximum frequency is 700 MHz.
Advantages of chip systems
The main purpose of using SOC in design involves the steps that form the benefits of the device:
- SOC is small in size but includes many features.
- Flexibility. In terms of chip size, power and form factor, these systems are very hard to beat by other devices.
- Cost efficiency, especially for specific SoC applications such as video code.
- The system-on-chip is countless. For high-capacity products, they simplify resource protection and engineering costs.
However, such an excellent device has its drawbacks:
- Large time investment. The SoC design process can take anywhere from 6 to 12 months.
- Limited resources.
- If a low volume product is being developed, high end equipment will be required. It may be better to use third party hardware, spend time and resources on application software.
Systems on a chip have the big disadvantage that they cannot be adaptable at all. In other words, they cannot be upgraded. A system on a chip usually dies the same as it was created. Nothing changes in it during the entire service life. If something breaks internally in the appliance, only that part cannot be repaired or changed. Have to replace the entire SoC.
The largest producersmobile chips
We offer a brief overview of SoCs from major manufacturers: Qualcomm, Samsung, MediaTek, Huawei, NVIDIA and Broadcom. Qualcomm, NVIDIA, and MediaTek manufacture and sell primarily mobile SoCs for hardware companies to use in devices they manufacture. Broadcom makes SoCs that are used in routers and networking devices, and Samsung and Huawei not only make SoCs, but are the two largest companies in the world in using them.
You can't say which system on a chip is the best. The design and development of systems-on-a-chip is moving so fast that by the time of comparison, the option will already be obsolete. However, you need to remember that the best SoC may not be the best for processors or the fastest wireless transfers.